Parallel processing¶
Generality¶
pyqcm could benefit from various methods to perform parallel processing in shared memory system. Three parallelisations method could be used in theory:
Those implemented in BLAS/LAPACK,
Those implemented in the CUBA numerical integration library
And those implemented in QCM library (with OpenMP).
By default, pyqcm (and QCM) disable parallelization using BLAS/LAPACK and CUBA, to use its own implementation using OpenMP with all the cores available on the machine. Users can still specify fewer number of core to use by exporting the environment variable OMP_NUM_THREADS, e.g.:
OMP_NUM_THREADs=X #use X cores
User can also choose to rely on the CUBA library parallelization by setting the environment variable CUBACORES. QCM OpenMP parallelization must also be unset:
CUBACORES=X #use X cubacores, X must be >=2
OMP_NUM_THREADs=1 #unset OpenMP
However, using this method, only the integration section would be treated in parallel.
Performance¶
The following Figure 1 compares parallelization performance on a simulation which spend most of its time (i.e. more than 99% using a single core) in the numerical integration. Tests were performed on a 2 x Intel Xeon Gold 6238 Cascade Lake @ 2.10GHz with 22 cores each and HyperThreading disabled.
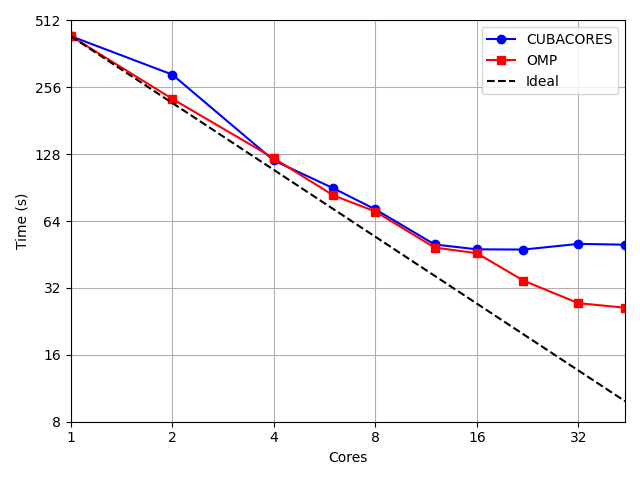
Figure 1: Parallel performance using QCM OpenMP (in red) and Cuba parallelization (in blue).¶
User should note that while OpenMP used the same object in memory to perform calculation in parallel, CUBA rather duplicate the object in the memory, resulting in a significant memory consumption.